Fluorometry studies of aptamers that bind intrinsically fluorescent ligands: techniques, obstacles and optimizations
PROTOCOL
![]()
ISSN: 2514-3247
Aptamers (2022), Vol 6, 19-27
Published online: 26 September 2022
Full Text (Shoara ~1740kb) | (PubMed Central Record HTML) | (PubMed) | (References)
Aron A Shoara and Philip E Johnson*
Department of Chemistry and Centre for Research on Biomolecular Interactions, York University, Toronto, Ontario, M3J 1P3, Canada
*Correspondence to: Philip Johnson, Email: pjohnson@yorku.ca, Tel: 1 416 736 2100 x33119
Received: 22 June 2022 | Revised: 03 September 2022 | Accepted: 26 September 2022
© Copyright The Author(s). This is an open access article, published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0). This license permits non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction of this article, provided the original work is appropriately acknowledged, with correct citation details.
ABSTRACT
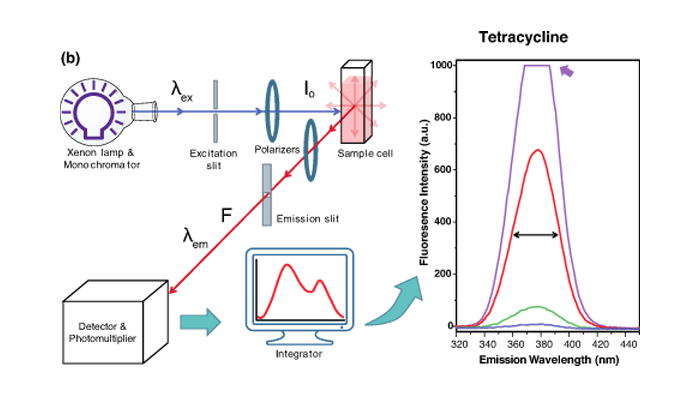
Intrinsic fluorescence analysis is a sensitive technique to gain insight about aptamer-small molecule interactions. Employing fluorescence properties of the ligand, the binding affinities of the aptamer-ligand complex can be quantified in the nM to mM range with great accuracy and precision. Here, we present a detection method for aptamer-ligand binding analysis that is based on the inherent fluorescence of the ligand. Further, we discuss how to optimize and resolve some common experimental challenges.
KEYWORDS: Aptamers, fluorometry, fluorescence properties, binding affinity
