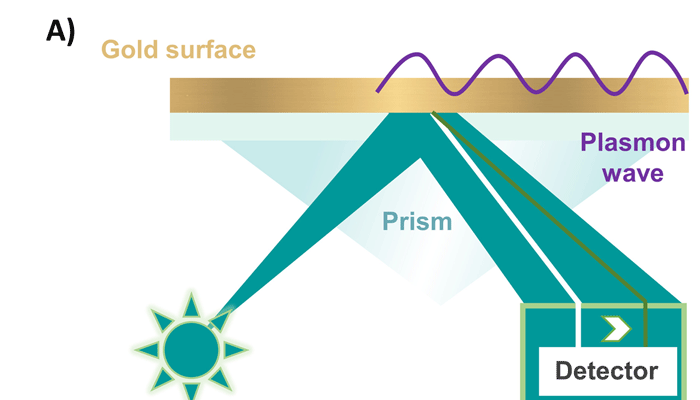
Surface plasmon resonance assay for screening diverse aptamer-target interactions
MINIREVIEW
![]()
ISSN: 2514-3247
Aptamers (2023), Vol 7, 7-12
Published online: 23 March 2024
Full Text (Ayon ~1250kb)
Omma Shahara Ayon1 and Maureen McKeague1,2,*
1Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, McGill University, Montreal, QC H3A 0B8, Canada
2Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, McGill University, Montreal, QC H3G 1Y6, Canada
*Correspondence to: Maureen McKeague, Email: maureen.mckeague@mcgill.ca
Received: 18 January 2024 | Revised: 15 February | Accepted: 15 February 2024 | Published: 23 March 2024
© Copyright The Author(s). This is an open access article, published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0). This license permits non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction of this article, provided the original work is appropriately acknowledged, with correct citation details.
ABSTRACT
Natural aptamers control biological processes in bacteria while synthetic nucleic acid aptamers have been applied to numerous biotechnological applications. Prior to developing aptamer technologies, sequence variants and specificity must be characterized. Here, we present a highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance (SPR) method adapted to rapidly screen aptamer variants against diverse molecules.
KEYWORDS: aptamer, surface plasmon resonance, aptamer-target interaction, equilibrium constant, binding assay, kinetics
